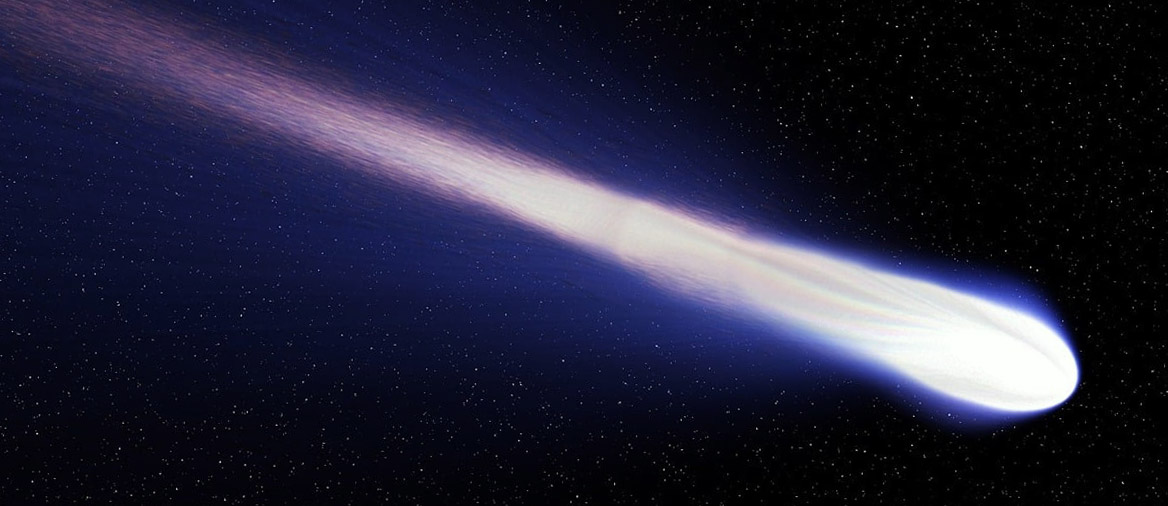
Comets are some of the most spectacular objects to look at in the Solar system. They are basically giant snowballs traveling through space leaving a trail of shiny dust. Watching them with a telescope is a great experience that I’d highly recommend to anyone.
The word comet comes from the Latin word comēta which means “to wear long hair”.
They also have a unique composition and origin, making them even more interesting.
That is why in this article we’ll learn more about them with this list of the unique characteristics of a comet. Let’s get started.
Comets are made of ice, rock, and gas
One of the most important characteristics of comets is their composition. Unlike asteroids, which are made of rock and metal, comets have a high percentage of ice water, and frozen gases like carbon dioxide, ammonia, methanol, and ethanol.
These materials are found in what is called the nucleus, which is the solid body of the comet.
The percentage of each material varies from comet to comet. The fewer frozen materials it has, the shorter the lifespan of the comet will be. More on that later.
Comets have a tail
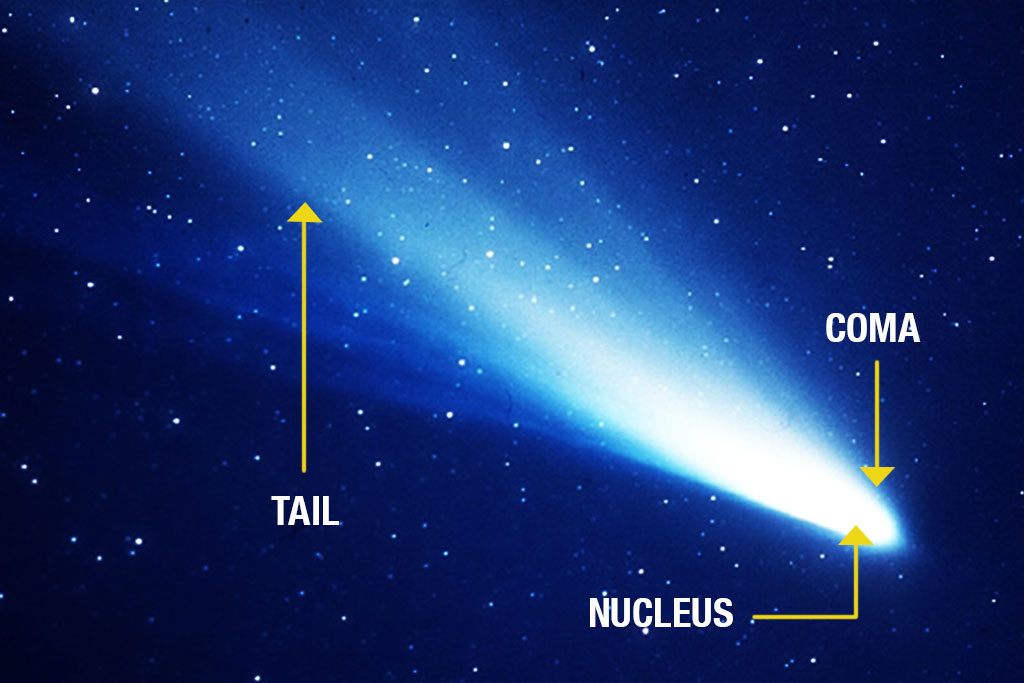
Comets orbit the Sun just like a planet or an asteroid. But as their trajectory gets them closer to the star, the heat from the Sun begins to vaporize the frozen parts of the comet.
And since comets are traveling at high speeds, they leave behind a trail of tiny particles of dust, vapor, and gas. When these little pieces reflect sunlight, it looks like they are glowing and that’s why it looks like they have a long tail.
Even though only the first part of the tail is visible at any given time, the tail of a comet can extend for millions of kilometers. Some tails have been measured to be longer than 3 times the distance between Earth and the Sun.
The comet’s tail and the coma (the glowing parts around the nucleus) are the parts of the comet that seem so bright and spectacular to us.
Comets have eccentric orbits
Most of the planets have orbits that are more or less circular. But smaller objects and objects that are farther away from the Sun, tend to have more elliptical orbits, or in scientific terms “they have a higher eccentricity”. Such is the case of comets.
This allows comets to survive for longer periods of time. Because the frozen parts only vaporize as they get closer to the Sun. If they had more circular orbits, they’d burn out much faster.
This is also the reason why comets take such a long time to be visible from Earth between apparitions. For example, Halley’s Comet is only visible from Earth every 76 years. Its next appearance won’t happen until 2061.
Most comets come from the Oort cloud
The Oort Cloud is a gigantic area located at the very end of the Solar system. It is many times farther away from the Sun than Pluto. It is believed that the Oort cloud contains trillions of comets and asteroids. But since it is so big and the objects in it are relatively small, it would be unlikely to run into one if you were to pass by.
Sometimes the orbits of these objects are affected by the gravity of passing stars, shooting them into the interior parts of the Solar system. Those are the comets that we see.
It is believed that comets actually formed much closer to the Sun but were ejected by gravitational interactions when the gas giants formed.
Other comets, the ones that have periods shorter than 200 years are believed to come from the Kuiper belt. An area full of asteroids like the asteroid belt but that is located beyond Neptune.
Very few comets are visible
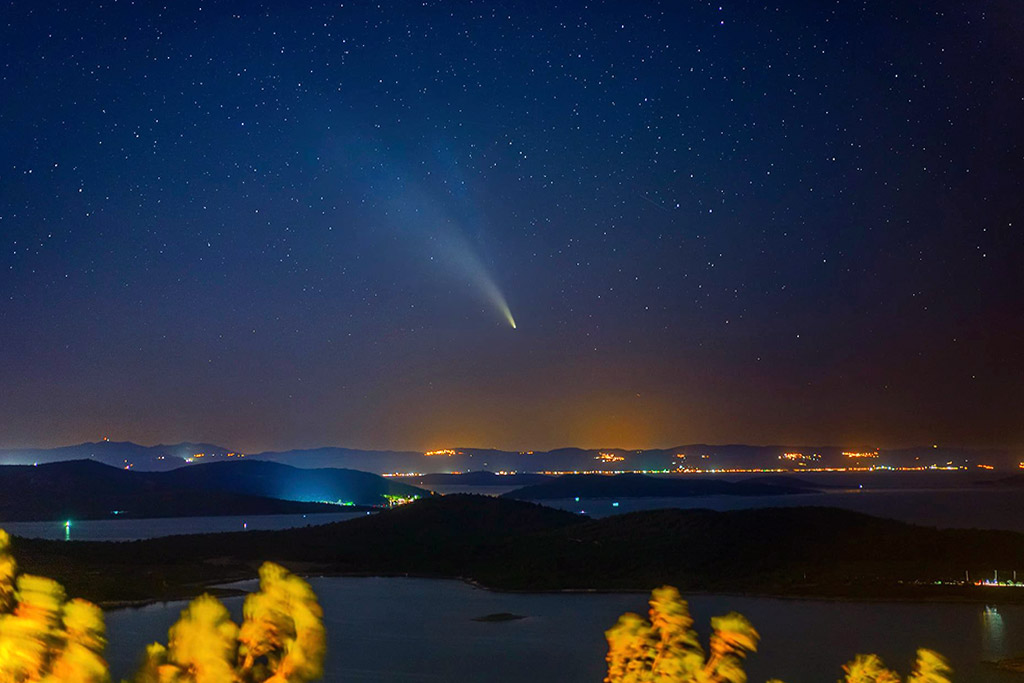

Comets are not visible too often from Earth. Especially not without the help of a telescope.
Every year only one or two comets are visible to the naked eye and usually only in areas with clear skies and low light pollution.
This might be the reason why ancient civilizations believed that comets were omens of good or bad luck, because they only occurred sparingly.
Comets don’t live long
This might be pretty obvious, but comets lose lots of ice and gas to vaporization every time they get close to the Sun. This means that comets don’t have a short lifespan compared to most celestial objects. The average comet only lasts for 20,000 years.
After a comet loses all of its ice only the rocky parts of the nucleus remain. At this point, the comet is then considered an asteroid. It is estimated that about 10% of near-Earth asteroids started out as comets.
But don’t worry, we will not run out of comets anytime soon because…
There are probably a trillion comets just in the Solar system
The Oort Cloud is estimated to be somewhere between 8,000 and 90,000 Astronomical Units long. One Astronomical Unit is the average distance between Earth and the Sun or about 147 million kilometers (91 million miles).
Astronomers believe that this huge bubble that surrounds the Solar system is full of small objects like comets. Scientists have calculated that the Oort Cloud could contain up to one trillion comets.
Comets are the cause of meteor showers
A comet’s tail leaves a long trail of dust and small pieces of rock and ice that remain floating in space.
Sometimes, Earth’s orbit passes by these areas and these pieces enter our atmosphere, becoming meteors. If they are big enough and there’s a large a number of them, they can be visible to us when they enter by the atmosphere and it lights them up because of the friction. This is what we call a meteor shower and it can be a beautiful astronomical show.
Most of these meteors are destroyed in the atmosphere, but every once in a while one will survive and land on Earth. Those are then called meteorites.
We have a whole article explaining meteor showers in-depth if you want to learn more about them.
Comets might have brought water to Earth
Just like asteroids, comets sometimes cross paths with a planet or a moon, and if they are big enough, they can crash violently into the surface.
Well, scientists believe this is exactly what happened to Earth millions or even billions of years ago. But with these comets came a lot of ice, and therefore, water.
There is a debate as to how much of Earth’s water came from comets. Some scientists believe it is only about 10% while others suggest it is a much higher percentage.
Comets are named after their discoverer
In popular culture, there is the misconception that the discoverer of a celestial object gets to name it. This is not true. Most categories of astronomical bodies have clearly defined naming conventions and guidelines set by the International Astronomical Union to avoid names becoming a disaster. I think we can all agree it’s not a great idea if a newly discovered exoplanet is baptized as “BillyWasHere421”.
The only category of objects that can still be named after the discoverer are comets, and even then there are rules. The comets can be named after up to three of their discoverers but still should receive a scientific designation that includes their orbit type, the year it was first spotted, and the order in which it was discovered. So the names of the comets end up being something like “Wilson C/1986 P1” or “Groeller P/2019 B2”.
Since these days most new comets are only discovered by large observatories, there’s hundreds of the named “SOHO” or “ATLAS” after the name of the telescope.
We have an article about comet names that explains more about this and contains a list of all known comets.
Enjoyed this article?
Get daily 10-minute PDFs about astronomy to read before bed!
Sign up for our upcoming micro-learning service where you will learn something new about space and beyond every day while winding down.