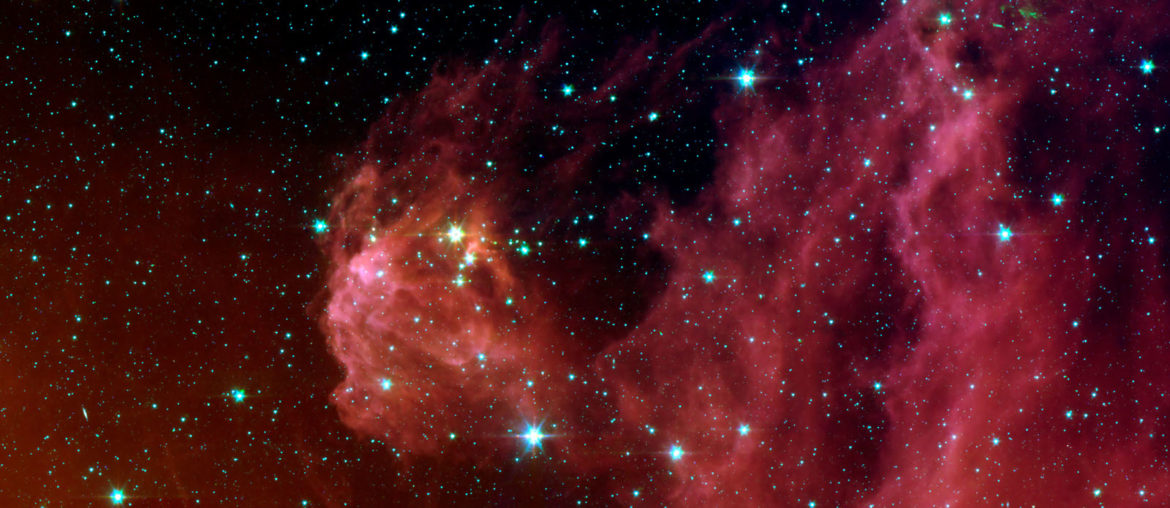
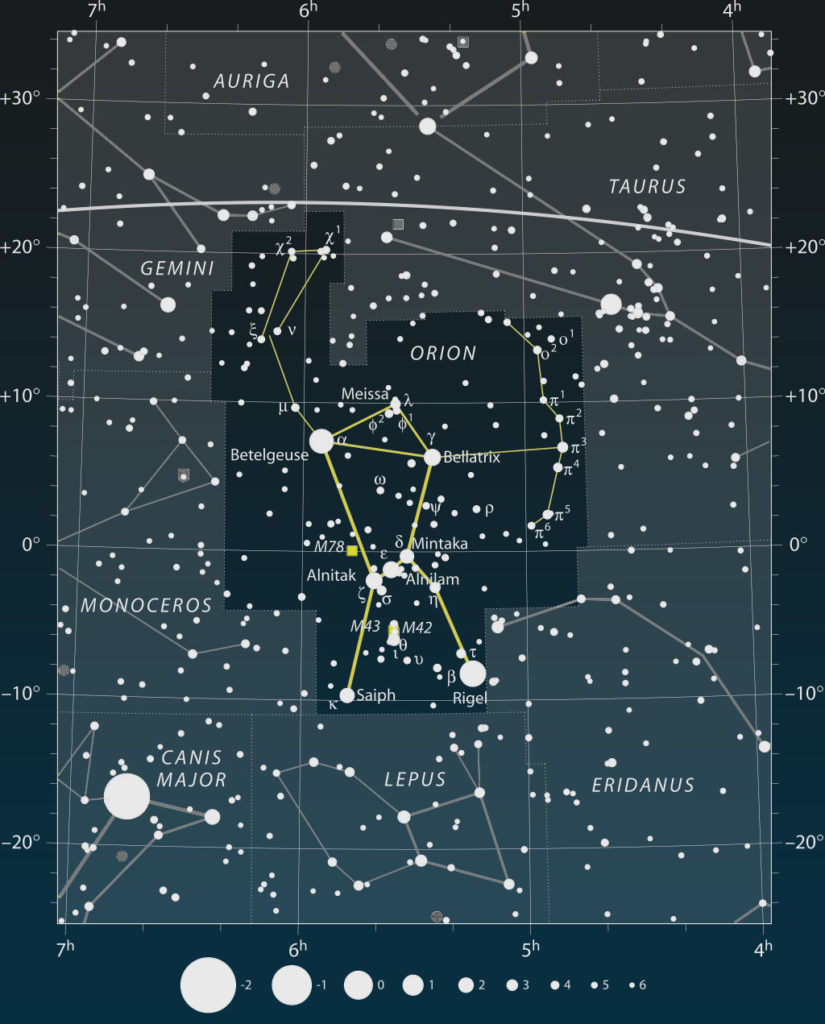
Orion is one of the most famous and recognizable constellations in the sky. It is visible from most parts of the world and has inspired many myths. Some civilizations had different names and legends for it, but the current name we use today is taken from Greek mythology and was named after the hunter Orion.
The constellation is formed by some of the brightest stars in the night sky, including three lined up stars in the middle that form Orion’s belt. This makes it very easy to locate and it is commonly used as a mark to find other stars and constellations around it.
Let’s take a look at some of the most important information of Orion in the following fact sheet.
Orion Fact Sheet
| Astronomical abbreviation | Ori |
| Named after | Orion the hunter (Greek mythology) |
| Main stars | 7 |
| Total stars | 88 |
| Stars that contain confirmed planets | 10 |
| Brightest star | Rigel (Also known as β Ori or Beta Ori) |
| Area | 594 square degrees |
| Quadrant | NQ1 (First Quadrant, Northern Hemisphere) |
| Visible in the Southern Hemisphere during | Summer |
| Visible in the Northern Hemisphere during | Autumn to Spring |
| Bordering constellations | Eridanus, Gemini, Lepus, Monoceros, Taurus |
Interesting Facts
Orion is one of our favorite constellations because its history is rich and full of curious things. Let’s take a look at some cool tidbits you can use to impress your friends the next time you are looking at the sky.
- The earliest human-made depiction of Orion that has been found is a mammoth Ivory carving found in a cave in Germany. Archaeologists believe it is about 38,000 years old. This tablet is also the oldest image of a star pattern.
- Rigel, the brightest star in the constellation and the one at the end of its left foot, is the seventh brightest star in the sky
- On Middle-Earth, from the Lord of the Rings books, Orion is referred to as Menelvagor, meaning “The swordsman of the sky”
- Orion is home to the Horsehead nebula, the protagonist of some of the most iconic photos of space.
- The name of the main character of the movie Beetlejuice is a play on the name Betelgeuse, the second brightest star in Orion (the one that forms its right shoulder)
- Speaking of Betelgeuse, scientists believe it will go Supernova and explode soon. By “soon”, we mean in astronomical terms, to be more accurate, in the next million years.
- One more about Betelgeuse: If human eyes could see all wavelengths of radiation, Betelgeuse would be the brightest star in the sky.
- Ok, last one about Betelgeuse, we promise its a cool one. If you could grab Betelgeuse and put it in the center of our Solar System, the star would extend all the way to the asteroid belt and maybe even Jupiter’s orbit. It is a red supergiant 887 times the size of our Sun.
- All the main stars in Orion are larger than the Sun. Even the smallest one, Bellatrix is almost 6 times the size of our Sun.
- Bellatrix is also the closest star in Orion to us. It is 250 lightyears away. The most remote one is Alnilam, which is 2,000 lightyears away.
- By the year 14,000 Orion will no longer be visible from Great Britain, Canada and places in the same latitude. This is due to natural changes in Earth’s rotational axis.
- Some archeologists believe the three largest Pyramids of Giza, in Egypt, were built to line up with the three stars that form Orion’s belt. The hypothesis is controversial as the angle isn’t an exact match.
- Every year, around the 20th of October a meteor shower happens on Orion’s location. Because of this, it was named the Orionid meteor shower, or Oriodnis.
- Rigel is not a single star, but a four-star system. The one we can see with the naked eye in the night sky is only Rigel A.
- Rigel B and Rigel C, two of the other stars on Rigel can be seen with the help of a telescope. Rigel B, in turn, might be a triple star system. It is stars within stars within stars all the way down!.
- In Spain, Mexico and other countries, the three stars in Orion’s belt are said to be the three wise men. These biblical kings bring gifts to well-behaved kids on January 6 every year.
What shapes do you see in Orion?
Many artists have drawn and painted different interpretations of how they view Orion in the night sky and there’s a bit of controversy as to what exactly is he carrying in his hands.
First, take a look at his right hand. It draws two long lines that make it look like it has a weapon. Some ancient artists drew him holding a sword, while more classical interpretations have him holding a club.
The same thing happens in his left hand. Some people say he is holding an animal’s pelt while others say he is holding a lion. If you ask me, I’m on a completely different boat as I see a bow which in my opinion goes very well with the idea of the hunter.
There’s no official interpretation as to what is Orion holding in his hands, but in Homer’s Odyssey, he is said to have a bronze club.
The three stars that are lined up in the middle of the constellation are said to be Orion’s belt.
If you only look at the major seven stars in Orion and remove all the other minor stars, it also looks like an hourglass.
Orion’s belt
You might have heard someone mention Orion’s belt as it is one of the most prominent features in the night sky. In case you don’t know what it is, it refers to the three stars in the middle of Orion that form a straight line and form a belt in the middle of the constellation. The three stars are Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. In contrast with the names of the other stars in the constellation which come mostly from Greek myths, the names of the stars in the belt have Arabic origins and mean “the girdle”, “sapphire” and “belt” respectively.
Mythology
The current name for Orion comes from Greek mythology. Orion was a legendary, strong, handsome hunter that once boasted he could kill every animal on the planet. The goddess Gaia got angry at him for this and sent a scorpion that stung him and killed him. For this reason, it is said the constellations of Orion and Scorpio are never in the sky at the same time.
Orion is the son of the god of the sea Poseidon (Neptune) and the princess of Crete, Euryale, which made him a demigod. A demigod is the child of a god or a goddess with a regular human.
It is also said that in the night sky, Orion can be seen chasing the Pleiades. The Pleiades were the seven daughters of Atlas and Pleione and it is said they were beautiful. In astronomy, the Pleiades is a star cluster in the Taurus constellation. According to the myth, Orion fell in love with them so Zeus placed the Pleiades in the sky. Because Orion and Taurus are close to each other, and all the stars in the sky move in the same direction, it does seem like Orion is chasing them.
An even older origin of Orion comes from Sumerian mythology where it was associated with the story of King Gilgamesh fighting the Bull of Heaven. As mentioned above, Orion is next to Taurus (the bull).
In Hungarian mythology, the constellation is known as Nimrod, also a legendary warrior, while the Chinese knew it as Shen.
Stars
Orion is composed of 88 stars, but only seven of those are considered major stars. The rest are smaller stars and most of them can only be seen with the help of a telescope or binoculars.
The following table details the name of Orion’s major stars, how far each of them are from Earth and how big it is compared to our Sun.
| Star Name | Distance in Lightyears | Radius (Times the radius of the Sun) |
| Betelgeuse | 643 | 887 |
| Rigel | 860 | 78.9 |
| Bellatrix | 250 | 5.75 |
| Mintaka | 1,200 | 16.5 |
| Alnilam | 2,000 | 42 |
| Alnitak | 1,260 | 20 |
| Saiph | 650 | 22.2 |
As you can see, Betelgeuse is the biggest star of the group and Bellatrix is the smallest one and also the closest one to us on Earth. Alnilam, one of the star’s in Orion’s belt is the one farthest away.
In Science-Fiction and Fantasy
Orion has been represented and used as inspiration in many different types of media. Here are some of the most notable ones.
- In the Harry Potter book and movie series, the name of the character Bellatrix Lestrange is taken from the star Bellatrix, one of the main stars in Orion.
- In the movie Men in Black, the plot revolves around the characters trying to figure out the phrase “The galaxy is in Orion’s belt” to save the planet.
- Betelgeuse, the main character from the movie Beetlejuice is named after Betelgeuse, the largest star in Orion.
Finding other stars using Orion
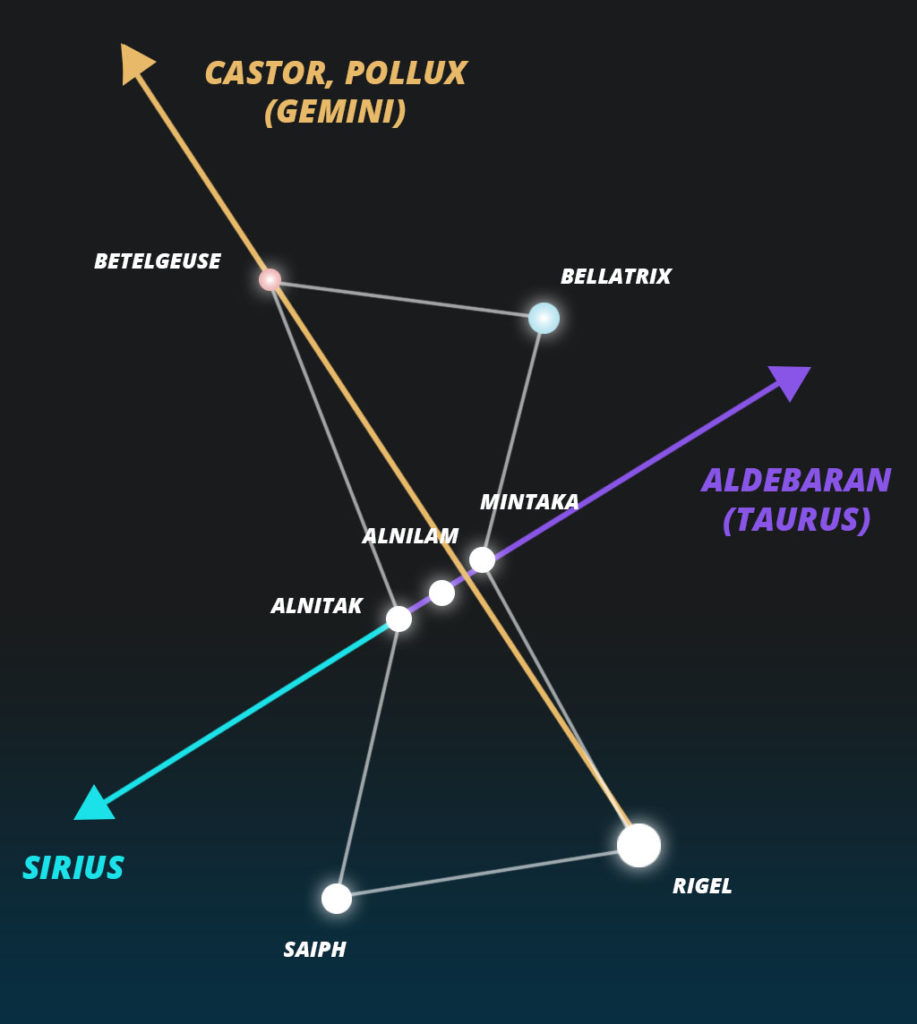
Because it is easy to find, Orion can be used as a navigational point in the sky to help you find other constellations and stars.
If you extend the imaginary line that forms Orion’s belt in the direction of Mintaka, it points directly to Aldebaran, or Alpha Tau, the brightest star in the Taurus constellation.
If you extend the same line to the opposite direction, it points to Sirius, the brightest star in the sky.
If you draw an imaginary line from Rigel to Betelgeuse and extend it, it points to the stars Castor and Pollux, part of the Gemini constellation.







