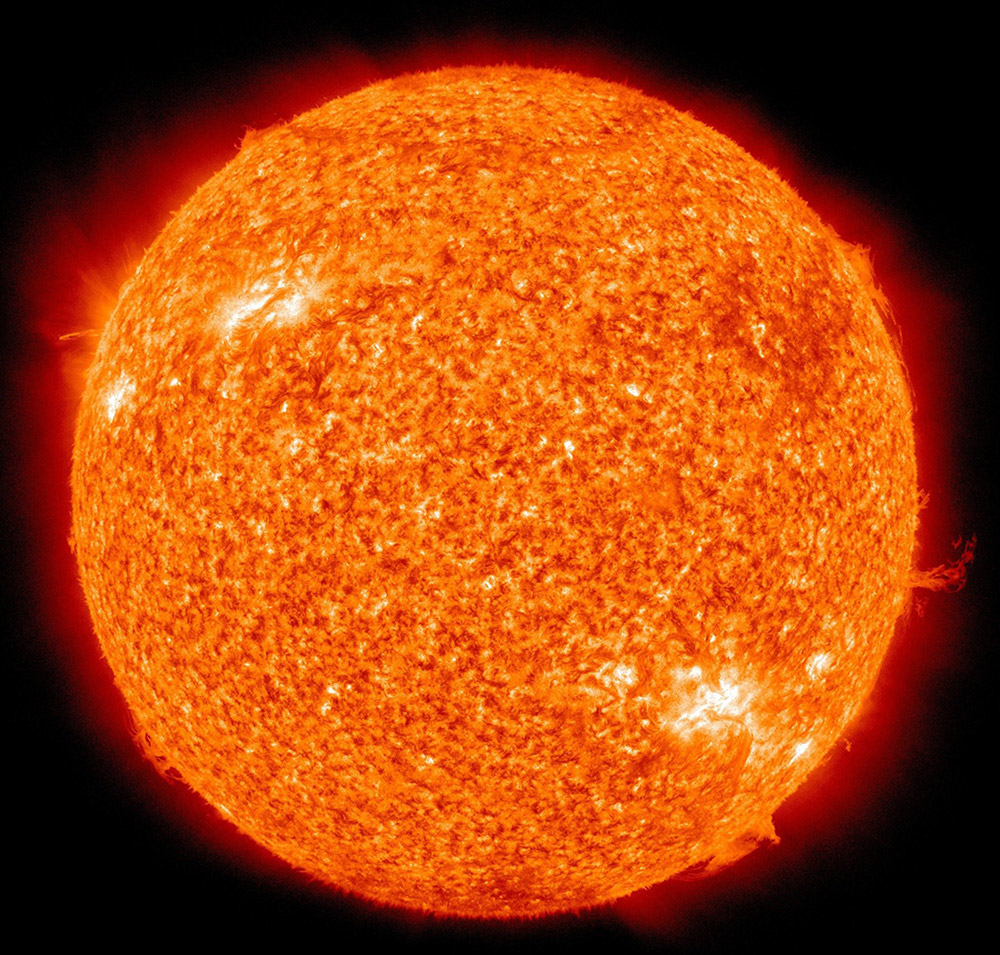
Stars are one of the key objects in the universe. They emit the light that allows us to perceive all the other things in space, they are the central components of solar systems, and some of them turn into the supermassive black holes that are at the core of galaxies.
This is why stars are very interesting and important to study. It is not too hard to distinguish them from other objects because the characteristics of a star are well-defined and unique. For example, if you check out our article about the differences between planets and stars you will see they have many distinct features.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the main characteristics of a star. These are the things that make them what they are and define them.
There are many types of stars, but they all share most of these features.
1) Stars emit their own light
Stars are the most common source of light in space (but not the only one). The process through which they shine starts at their cores. The gravitational force is so strong in the core of a star that it makes protons collide with each other. This process releases A LOT of energy in the form of heat and light that travels across space.
The light that stars release is not just the one we can see with our eyes or telescopes. They also emit light in the ultraviolet and infrared spectrum. These are wavelengths of light that humans can’t perceive with our eyes, but that we can detect using other instruments.
2) Stars produce thermonuclear fusion
The reason why stars are such big energy factories is because of the nuclear reactions that happen at their cores.
Stars are mostly made up of hydrogen. For example, it makes up 92.1% of our Sun.
When two hydrogen atoms collide at great speeds and fuse, they produce helium and release a huge amount of energy. This is what we call nuclear fusion and is where all the energy, light, and heat that stars produce comes from. Ok, the process is actually a bit more complicated than that, but for the sake of simplicity let’s leave it at that.
Because of the huge size of stars, the gravity at their core is constantly shooting the hydrogen atoms in all directions, resulting in this reaction.
3) Stars are (mostly) spherical
After a certain size that depends on their composition, objects in space will always tend to be shaped like a sphere. This is because that is the shape that minimizes the gravitational potential energy of the system, creating a hydrostatic equilibrium.
HYDROstatic? like water?
Yes, exactly like water. Solid objects that are large enough – even rocky ones like planets or moons – start to behave in certain ways like a liquid.
This is why all large objects in space are shaped like a sphere, including stars.
4) Stars rotate just like planets
The Earth rotates once on its own axis every 24 hours (approximately). This is what we call a day and the reason why there’s a day/night cycle.
Stars like the Sun also have a rotation period although it can be a bit different.
Because stars are made out of plasma, they are not fully solid bodies. This means their rotational speed can vary depending on what part of the star you are talking about. For example, the Sun’s rotation period is 24.4 days at its equator, but it is almost 38 days at the poles.
There are stars that rotate much faster than the Sun. For example, Regulus A, the brightest star in the Leo constellation, spins at a speed of 317 kilometers per second. It completes a full rotation in less than 16 hours even though it is almost 4 times bigger than the Sun. Regulus spins so fast that it causes it to bulge around the middle, making it look a bit like an egg.
5) Stars also travel through space
We are all taught that Earth orbits around the Sun. And that might get you to think that the Sun is stationary. But that’s far away from the truth.
Everything in the universe is moving. Moon orbit planets. Planets orbit stars. Stars orbit galactic cores or other stars. And so on.
The whole Solar system is moving along as the Sun moves.
The stars in our galaxy, like the Sun, travel through space orbiting the core of the galaxy, which is made up of a bar of other stars and a supermassive black hole. It takes the Sun approximately 230 million years to make a full orbit around the Milky Way.
Of course, all this movement means that sometimes stars end up colliding with each other, or sometimes one of them ends up being ejected and becomes a rogue star traveling through intergalactic space. There are many interesting interactions caused by stars moving through space.
6) Stars die
It is hard for us to imagine the Sun not being up in the sky one day. But just like stars have an origin, they also have an end. Even if millions or even billions of years have to pass for it to happen.
Most stars die because they run out of nuclear fuel, particularly hydrogen. Sometimes massive stars can use other elements like helium and carbon, but that is eventually exhausted too.
The fate and lifespan of stars depend on their size.
Massive stars die in a very violent way by exploding into a supernova that for a few weeks or months can be as bright as a whole galaxy. These stars don’t live for too long as they exhaust their hydrogen quickly.
Mid-sized stars, like our Sun, swell up for some time, destroying their planetary systems (if they have one) and turning into what is known as a red giant. The red giant slowly sheds its outer layers, leaving behind a nebula and a white dwarf, which is the core of what once was that star.
Smaller stars live the longest. They are called red dwarfs and scientists believe that some stars will live longer than the current age of the universe. Because of this, we don’t really know what the process of their death looks like, we haven’t found one that has died yet. We will have to wait a long time for one of them to die to see how it happens, but it is theorized that they will slowly – very slowly- cool off, leaving a white dwarf behind and the bigger ones might also form a nebula like mid-sized stars.
7) Stars are mostly made up of hydrogen (and other gases)
The main component of stars is also the most abundant element in the universe and the first element in the periodic table, hydrogen.
The Sun’s composition is estimated to be as follows:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 73% |
| Helium | 25% |
| Oxygen | 0.8% |
| Carbon | 0.36% |
| Iron | 0.16% |
| Neon | 0.12% |
| Nitrogen | 0.09% |
| Silicon | 0.07% |
| Magnesium | 0.05% |
| Sulphur | 0.04% |
| Traces of other elements | 0.04% |
While hydrogen is also the most abundant element in all stars, the percentages vary depending on the size and age of each individual star. On average, the element composition of most stars is:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 90% |
| Helium | 9% |
| Traces of other elements | 1% |
8) Stars are very, very hot
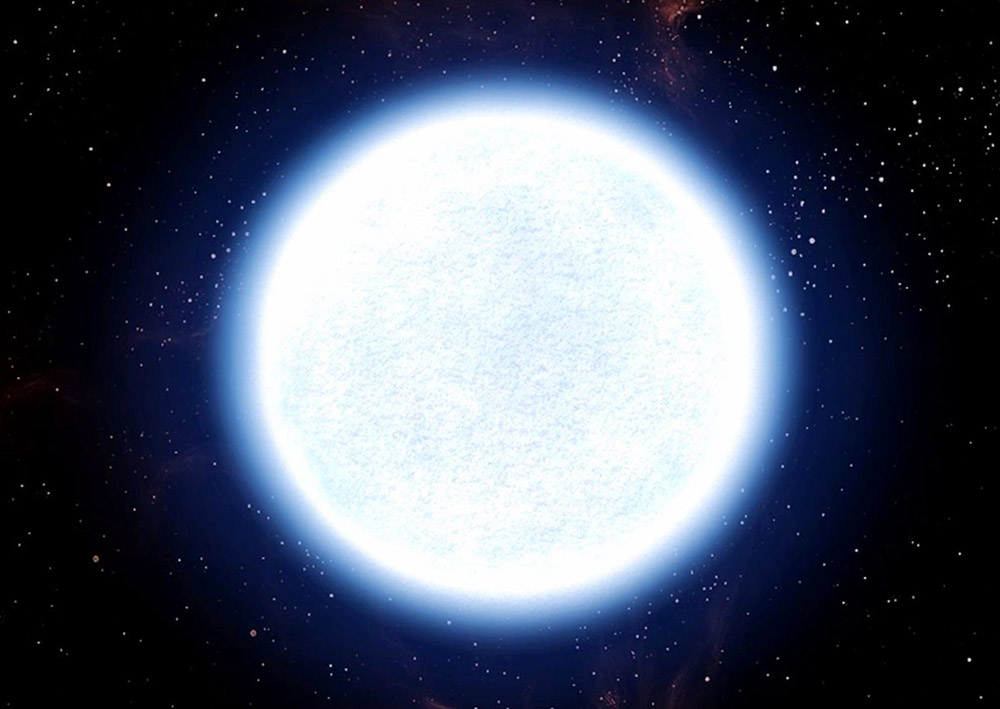

Every star has a different surface temperature that depends mostly on its mass. But even the smaller stars called red dwarfs that are a fraction of the size of our Sun (which isn’t really big, to begin with) can reach an average surface temperature of 3,225°C (3,500°K).
The average temperature for each star type is shown in the next table.
| Star type / color | Spectral Class | Temperature | Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | C | 3,225°C | 3,500°K |
| Orange | K | 5,025°C | 5,300°K |
| Yellow | G | 5,525°C | 5,800°K |
| White | F | 6,925°C | 7,200°K |
| Blue-White | A | 9,225°C | 9,500°K |
| Blue | B | 30,725°C | 31,000°K |
| Blue | O | 40,725°C | 41,000°K |
The table is ordered from the smaller to the larger types of stars. For comparison, the sun is a G-type yellow star. As you can see, it is right in the middle in terms of both size and temperature.
9 ) Stars can have many colors
Stars have many colors. The color of a star is going to be determined by its mass and temperature.
The colder stars are generally red. This can happen because they are small, slow-burn stars or because they have already exhausted most of their hydrogen.
The hottest stars are blue. These stars tend to live less time because they are bigger and “burn” their fuel faster.
The possible colors of a star are:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- White
- Blue
Enjoyed this article?
Get daily 10-minute PDFs about astronomy to read before bed!
Sign up for our upcoming micro-learning service where you will learn something new about space and beyond every day while winding down.